A depreciation checklist for commercial property owners and tenants
Contact
A depreciation checklist for commercial property owners and tenants
It can be hard to understand the tax depreciation allowances that are available to owners and tenants of commercial property, so BMT Tax Depreciation has compiled a checklist for owners and tenants of commercial property.
There are many rules which apply and the difference in depreciation found can vary depending on the industry, assets and property. By becoming more aware of commercial depreciation, property owners and tenants can make more informed financial decisions and improve their cash flow.
So, what is depreciation? Property depreciation refers to the natural wear and tear that occurs to a building and the assets within it over time. Australian Taxation Office (ATO) legislation allows the owner of any income producing property to claim this depreciation in two ways, as capital works deductions or depreciation for plant and equipment assets.
Capital works deductions
Capital works deductions apply to the structural elements of a building such as:
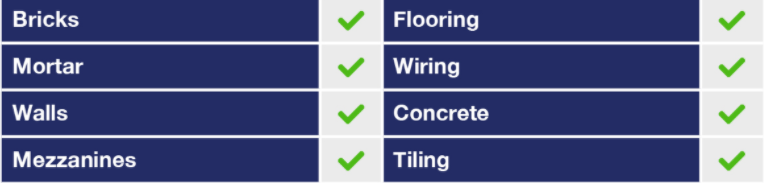
These deductions are based on the historical costs of the building and, apart from traveller accommodation, can only be claimed on commercial buildings in which construction commenced after 20 July 1982. Capital works deductions for traveller accommodation can be claimed on buildings in which construction commenced after 21 August 1979.
Plant and equipment depreciation
Plant and equipment assets are the removable assets within an income-producing property. Examples of assets which are commonly found in commercial properties include:
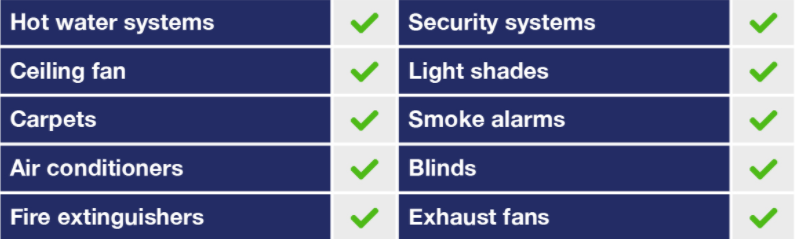
Depreciation for plant and equipment assets is calculated based on the individual effective life of each item as set by the ATO. The effective life of assets can also vary from industry to industry, so it is important to consult with a specialist Quantity Surveyor such as BMT Tax Depreciation to ensure deductions are calculated accordingly.
BMT offer a handy app called Rate Finder which allows you to search the effective life of any depreciable asset by name or industry. It’s available online or as an app.
What’s a tax depreciation schedule?
A tax depreciation schedule is a report that details all the available deductions in an income-producing property. It is prepared by a Quantity Surveyor and helps to boost property owners’ and commercial tenants’ cash flow. When preparing a schedule, a Quantity Surveyor will need the following information:
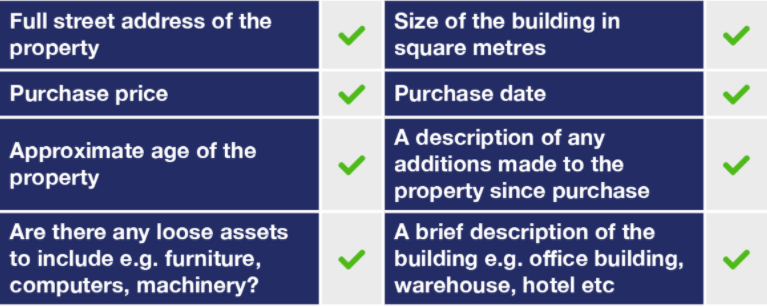
Due to the variety of commercial property types, a specialist site inspector will conduct a thorough inspection to measure the building and floor coverings, note down the construction method, workmanship, materials used and condition of the property. A Quantity Surveyor will use this information to maximise depreciation deductions.
A BMT Tax Depreciation Schedule lasts forty years, considers industry-specific legislation, provides a range of depreciation methods and includes a property inspection. The schedule is 100 per cent tax deductible and allows owners and tenants to boost their cash flow.
To maximise the cash return from your commercial property or business, simply Request a Quote today.
This is a sponsored article from BMT Tax Depreciation.
More from BMT Tax Depreciation:
Commercial property: frequently asked depreciation questions







